

—Produits—
 Téléphone +8618073152920
Téléphone +8618073152920 WhatsApp:+8615388025079
Address:Chambre 102, District D, Parc industriel de Houhu, District de Yuelu, Ville de Changsha, Province du Hunan, Chine
Connaissances produit
Temps:2025-08-06 17:26:25 Popularité:296
Les stations météorologiques agricoles sont des outils technologiques indispensables à l'agriculture moderne. Grâce à la surveillance en temps réel, à l'analyse des données et à une gestion intelligente, elles apportent un soutien scientifique aux agriculteurs et aux experts agricoles, les aidant à optimiser la production, à faire face aux catastrophes naturelles et à promouvoir un développement agricole durable. Cet article présente en détail les fonctions essentielles des stations météorologiques agricoles et leur rôle clé dans l'agriculture.
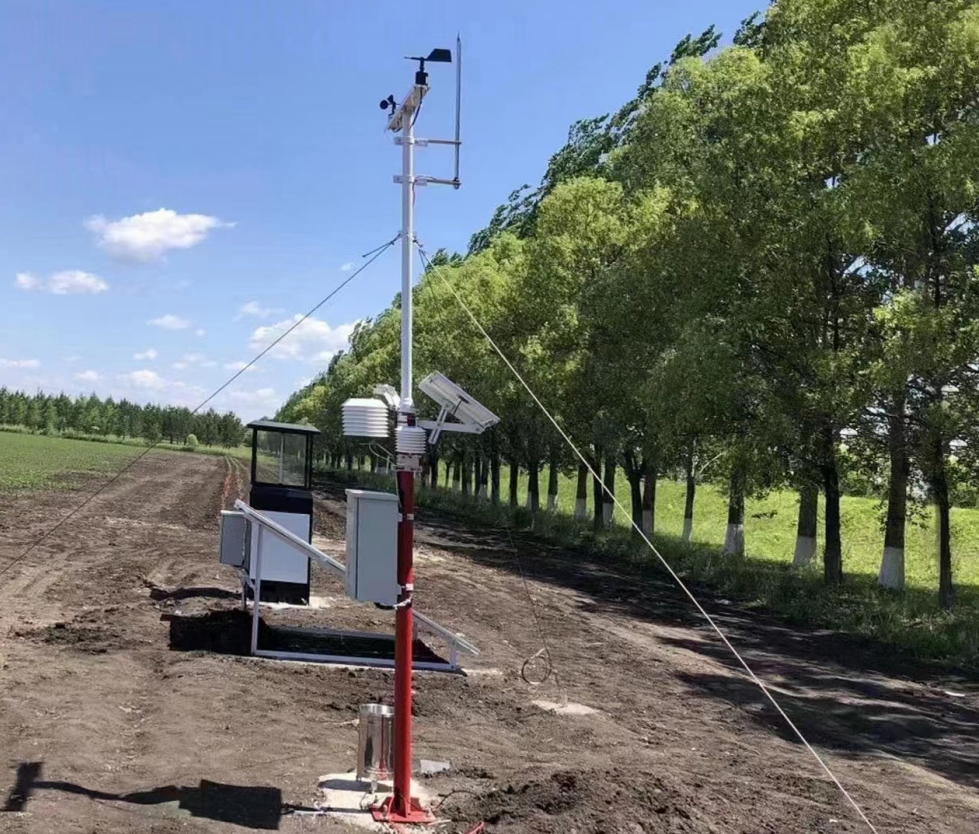

Les stations météorologiques agricoles intègrent divers instruments de haute précision pour surveiller l'environnement agricole et fournir des données complémentaires. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une analyse complète des fonctions et des valeurs des capteurs courants des stations météorologiques agricoles, notamment la température et l'humidité de l'air, la vitesse et la direction du vent, les précipitations, la température et l'humidité du sol, et le pH du sol.
Outil essentiel de l'agriculture intelligente, les stations météorologiques agricoles s'appuient sur de multiples capteurs de haute précision pour surveiller en continu les paramètres environnementaux clés des terres agricoles. Ces capteurs fournissent non seulement des données en temps réel, mais constituent également un atout précieux pour optimiser la production agricole, améliorer les rendements des cultures et s'adapter aux changements environnementaux. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une analyse détaillée des fonctions et des valeurs des capteurs courants des stations météorologiques agricoles : température et humidité de l'air, vitesse et direction du vent, précipitations, température et humidité du sol, et pH du sol.
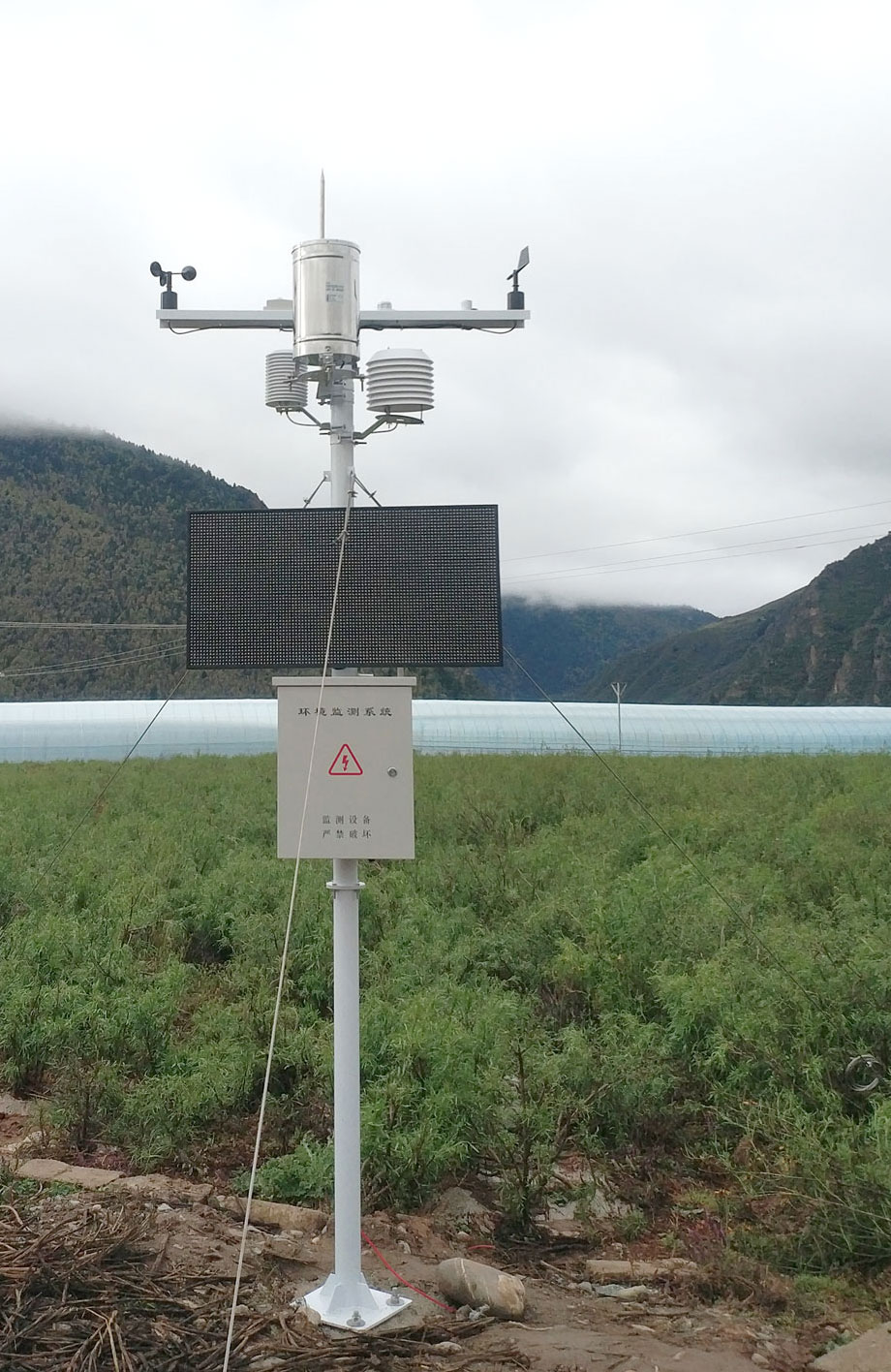

Fonction:
Les capteurs de température et d'humidité de l'air mesurent la température et l'humidité relative de l'environnement agricole en temps réel, reflétant avec précision le niveau de confort de croissance des cultures. Ces paramètres sont des facteurs cruciaux qui influencent la photosynthèse, la respiration et l'absorption d'eau des plantes.
Valeur:
- Optimizing Growth Conditions: Different crops have varying temperature and humidity requirements. For example, rice thrives in high-temperature and high-humidity environments (25-35°C), while wheat prefers cooler conditions (15-20°C). Real-time monitoring allows farmers to determine whether the current environment is suitable for crop growth and take measures (such as ventilation or humidification) to adjust it.
- Disease Prevention: High humidity is often associated with fungal diseases (such as rice blast). Sensor data helps farmers identify abnormal humidity levels early, allowing them to apply pesticides or improve field ventilation to reduce disease incidence.
- Energy Management: In greenhouse agriculture, temperature and humidity data can be linked to automated control systems to precisely adjust heating or humidification equipment, preventing energy waste.
Function:
Wind speed and direction sensors measure the wind speed and flow direction above the farmland. These data directly influence the rate of water evaporation, seed dispersal, and the spread of pests and diseases.
Value:
- Water Management: Strong winds accelerate the evaporation of water from soil and crops, especially in arid regions. By monitoring wind speed, farmers can schedule irrigation more effectively to prevent excessive water loss.
- Pest and Disease Control: Wind direction and speed affect the spread of pests (such as aphids) or pathogens. For example, if a sensor detects that the wind is likely to carry pests into the farmland, farmers can set up protective nets or apply pesticides in advance.
- Spraying Optimization: In pesticide or fertilizer spraying operations, high wind speeds may cause the spray to drift, reducing its effectiveness. Sensor data helps farmers choose the best spraying time to improve resource utilization and reduce environmental pollution.
Function:
Rainfall sensors measure the amount of precipitation over a unit of time, providing accurate data on natural water supply to the farmland. This information is critical for irrigation and drainage decisions.
Value:
- Smart Irrigation: Rainfall data helps farmers determine whether irrigation is necessary. For example, in dry periods with insufficient rainfall, the data allows precise calculation of irrigation amounts, avoiding water waste.
- Drainage Management: In areas with heavy rainfall, excessive precipitation may lead to waterlogging, threatening crop root health. Sensors provide early warnings to help farmers clear drainage systems and reduce flooding damage.
- Yield Prediction: Rainfall is closely related to crop yields. By accumulating long-term data, farmers and researchers can analyze the impact of rainfall patterns on yields and optimize planting plans.
Function:
Soil temperature and moisture sensors are embedded in the soil to monitor the temperature and moisture content in the root zone in real-time. These parameters directly reflect the soil environment's support for crop root growth.
Value:
- Root Health Assessment: Soil temperature affects root metabolic activity. For example, corn growth is hindered when soil temperature drops below 10°C. Moisture content determines whether water supply is sufficient. Sensor data helps farmers assess whether root growth conditions are ideal.
- Precise Irrigation: By monitoring soil moisture, farmers can avoid over-irrigating or under-irrigating. For example, when moisture is below the crop's required threshold, the system can automatically activate drip irrigation equipment, improving water use efficiency.
- Optimal Planting Timing: Soil temperature is an important factor in determining sowing time. For example, before spring sowing, farmers can check sensor data to ensure the soil temperature reaches a suitable level (e.g., above 15°C) for seed germination.
Function:
Soil pH sensors measure the soil's acidity or alkalinity, typically on a scale of 0 to 14, reflecting the soil’s chemical properties. This parameter has a profound impact on nutrient absorption and crop growth.
Value:
- Nutrient Absorption Optimization: Soil pH affects the availability of nutrients. For example, low pH (acidic soil) can lead to an excess of iron, aluminum, and other elements, inhibiting the root's absorption of phosphorus and potassium. High pH (alkaline soil) may lack trace elements. Sensor data helps farmers adjust soil pH by applying lime or sulfur, optimizing nutrient supply.
- Crop Adaptability Assessment: Different crops adapt to different soil pH levels. For example, blueberries prefer acidic soil (pH 4.5-5.5), while alfalfa thrives in neutral to slightly alkaline soil (pH 6.5-7.5). By monitoring pH levels, farmers can select crops that are best suited to local soil.
- Long-term Soil Management: Continuous monitoring of pH values helps track soil quality changes, preventing acidification or alkalization caused by long-term fertilization or rainfall, thus maintaining the soil's sustainable productivity.
In addition to providing immediate decision-making support, these sensors also provide data for long-term research. Scientists can analyze the relationship between soil pH and rainfall, for example, to develop crops that are more tolerant to acidic conditions, thus advancing sustainable agricultural development.
The air temperature and humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, soil temperature and moisture, and soil pH sensors are the core components of agricultural meteorological stations. Through real-time monitoring and data analysis, they provide farmers with accurate environmental information, helping optimize crop management, reduce natural risks, and improve production efficiency. These data are updated in real-time, providing users with dynamic “snapshots” of the farming environment, forming the foundation for agricultural management.
Agricultural meteorological stations are not just a set of equipment, but the backbone of modern agriculture. Below are their specific values in global agriculture:
Agriculture is greatly influenced by weather, and every step, from sowing to irrigation to harvest, requires accurate meteorological information. The real-time data provided by agricultural meteorological stations acts as a “health monitor” for crops, helping farmers plan agricultural activities wisely. For example, in areas with insufficient rainfall, drought warnings from the station can guide irrigation planning to avoid crop yield reduction.
Extreme weather events such as flooding, frost, or high temperatures can seriously threaten agriculture. Agricultural meteorological stations provide early warnings, giving farmers time to take countermeasures, such as reinforcing drainage systems or covering crops. This preventive capability is particularly important in today’s increasingly volatile climate.
Water and fertilizers are crucial inputs in agricultural production, but excessive use can increase costs and harm the environment. Agricultural meteorological stations guide irrigation and fertilization based on precise data, preventing waste. For example, when soil moisture is sufficient, the system will suggest pausing irrigation, saving water resources and reducing soil pollution.
Long-term meteorological data offer scientists the opportunity to study the impact of climate change on agriculture. For example, by analyzing years of rainfall and temperature records, more drought- or heat-tolerant crop varieties can be developed. These research results contribute to the improvement of agricultural adaptability and sustainability.
Globally, smart agriculture is becoming a trend. Agricultural meteorological stations, as data sources, combine with technologies such as drones and automation devices to build a smart agricultural ecosystem. This integrated management not only increases production efficiency but also provides small-scale farmers with opportunities to compete with large enterprises.

Les stations météorologiques agricoles constituent l'épine dorsale technologique de l'agriculture moderne. Grâce à la surveillance en temps réel, à l'analyse des données et à une gestion intelligente, elles aident les agriculteurs à faire face aux aléas climatiques, à améliorer l'efficacité de leur production et à protéger l'environnement. Des champs aux laboratoires de recherche, leur rôle est omniprésent. Qu'il s'agisse de lutter contre le changement climatique ou de promouvoir le développement d'une agriculture intelligente, les stations météorologiques agricoles démontrent leur valeur irremplaçable. À mesure que la technologie évolue, elles offriront encore plus de possibilités à l'agriculture mondiale, contribuant ainsi à l'atteinte des objectifs de développement durable de l'humanité.
Précédent:Classification et application des équipements de surveillance météorologique
Suivant:Stations météorologiques agricoles et stations de surveillance automatique forestière
Recommandations associées
Catalogue des Capteurs & Stations Météo
Catalogue des Capteurs Agricoles et Stations Météo - NiuBoL.pdf
Catalogue des Stations Météo - NiuBoL.pdf
Catalogue des Capteurs Agricoles - NiuBoL.pdf
Related products
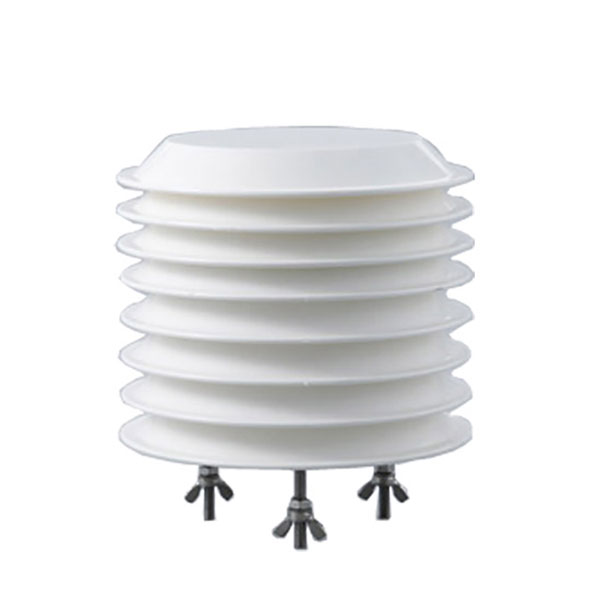 Capteur combiné de température de l'air et d'humidité relative
Capteur combiné de température de l'air et d'humidité relative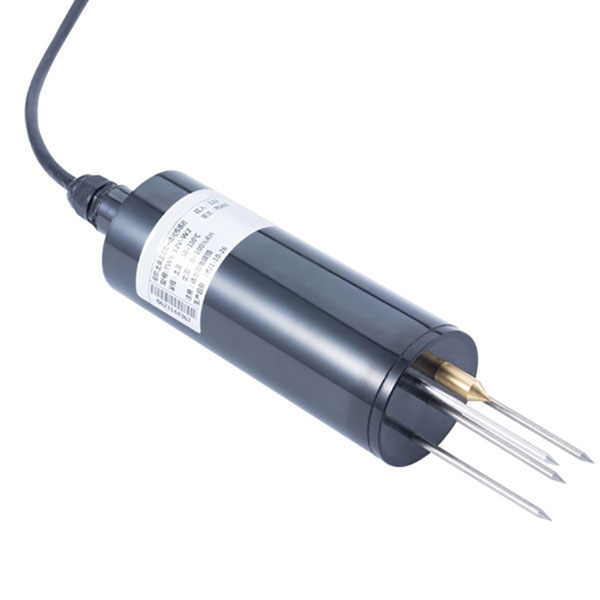 Capteur de température et d'humidité du sol pour l'irrigation
Capteur de température et d'humidité du sol pour l'irrigation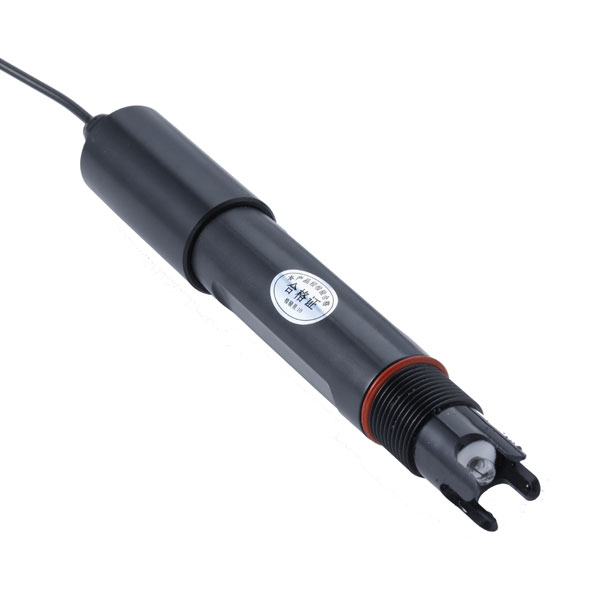 Capteur de pH du sol RS485, instrument de test du sol, pH-mètre pour l'agriculture.
Capteur de pH du sol RS485, instrument de test du sol, pH-mètre pour l'agriculture.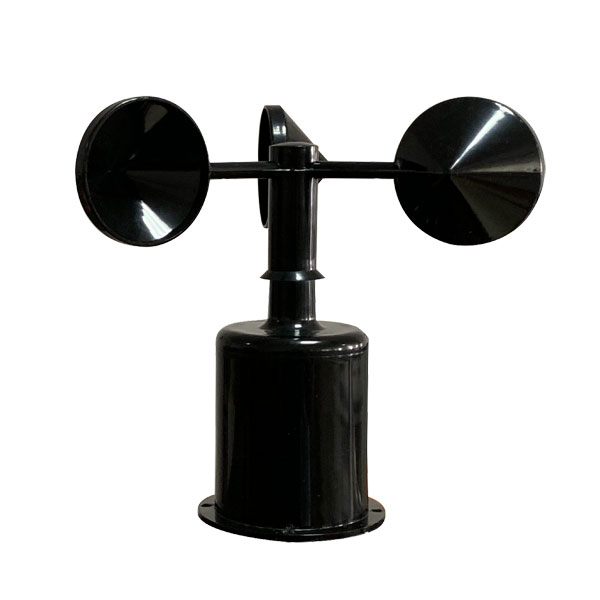 Capteur de vitesse du vent Sortie Modbus/RS485/Analogique/0-5V/4-20mA
Capteur de vitesse du vent Sortie Modbus/RS485/Analogique/0-5V/4-20mA Pluviomètre à auget basculant pour la surveillance météorologique capteur automatique de précipitations RS485/···
Pluviomètre à auget basculant pour la surveillance météorologique capteur automatique de précipitations RS485/··· Pyranomètre Capteur de rayonnement solaire 4-20mA/RS485
Pyranomètre Capteur de rayonnement solaire 4-20mA/RS485
Capture d'écran, WhatsApp pour identifier le code QR
Numéro WhatsApp:+8615388025079
(Cliquez sur WhatsApp pour copier et ajouter des amis)
